In the age of connectivity, Wi-Fi has become as essential as electricity in homes and businesses. However, even the most powerful routers can have difficulty covering an entire area with a strong signal. This is where Wi-Fi extenders come into play. A Wi-Fi extender, also known as a repeater, boosts the signal from your router to extend its reach to those hard-to-reach places.
A Wi-Fi extender works by receiving the existing signal from your router and re-broadcasting it to areas where the signal is weak or nonexistent. This process is relatively simple and can significantly improve your Wi-Fi coverage. However, the placement of the extender is crucial. It should be positioned halfway between your router and the dead zone for optimal performance.
When selecting a Wi-Fi extender, it's essential to match or exceed your router's Wi-Fi generation to ensure compatibility and performance. Modern extenders support newer Wi-Fi standards like 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) and 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), which offer improved range and speed over older standards.
Setting up a Wi-Fi extender is typically straightforward. Most extenders come with a setup guide that involves connecting to the extender's network, accessing its setup page through a web browser, and following the on-screen instructions. This process includes selecting your existing Wi-Fi network and entering the network password. Once configured, the extender will reboot, and you'll be ready to enjoy an extended Wi-Fi network.
WiFi Extender Tips:
-Place the Extender at the Half-Way Point - To avoid overlap with the router's signal or a weak connection to the extender, find the sweet spot roughly halfway to the dead zone. Some extenders will indicate whether the link is too weak, in that case move the extender closer to the WiFi router.
-Place It Up High - Wi-Fi signals travel better when the extender is placed in a higher position, away from obstructions and large appliances.
- Always use a Dual-Band Extender: A dual-band extender can provide a separate channel for communication, reducing interference and improving performance.
- Always, Always, Always use the 5GHz band over 2.4Ghz for the backhaul link as well as for general WiFi use.
Larger Homes
For those looking for an even more robust solution, mesh Wi-Fi systems offer an alternative to traditional extenders. These systems consist of multiple units that work together to create a seamless network.
Wi-Fi Extenders vs. Mesh Systems: Understanding the Differences
In the quest for a robust home Wi-Fi network, two popular solutions often come up: Wi-Fi extenders and mesh systems. While both aim to improve Wi-Fi coverage, they operate on different principles and are suited for different types of environments.
Wi-Fi Extenders: Bridging the Gap
Wi-Fi extenders, also known as repeaters, work by capturing the existing signal from your router and rebroadcasting it to areas with weak or no signal. They are simple devices that can be plugged into an outlet and are relatively inexpensive. The key to their effectiveness is placement; they need to be located within the range of your router's signal to be able to extend it further.
However, extenders have their limitations. The signal they rebroadcast is typically weaker than the original signal, and the further the extender is from the router, the more the signal degrades. This can result in slower internet speeds in the extended network area. Additionally, most extenders create a separate network SSID, which means you may have to manually switch between your main network and the extender's network as you move around your home.
Mesh Systems: Seamless Connectivity
Mesh Wi-Fi systems, on the other hand, consist of a series of nodes or satellites that work together to form a single, seamless Wi-Fi network throughout your home. Unlike extenders, mesh systems are designed to communicate with each other, creating a unified network with the same SSID and password. This allows for seamless roaming, as your devices automatically connect to the strongest signal without any manual intervention.
Mesh systems are generally more advanced than extenders, offering features like self-healing networks, where the system automatically finds the best path to route data in case one node fails. They are also scalable, meaning you can add more nodes to cover larger areas. However, this sophistication comes at a higher cost compared to traditional extenders.
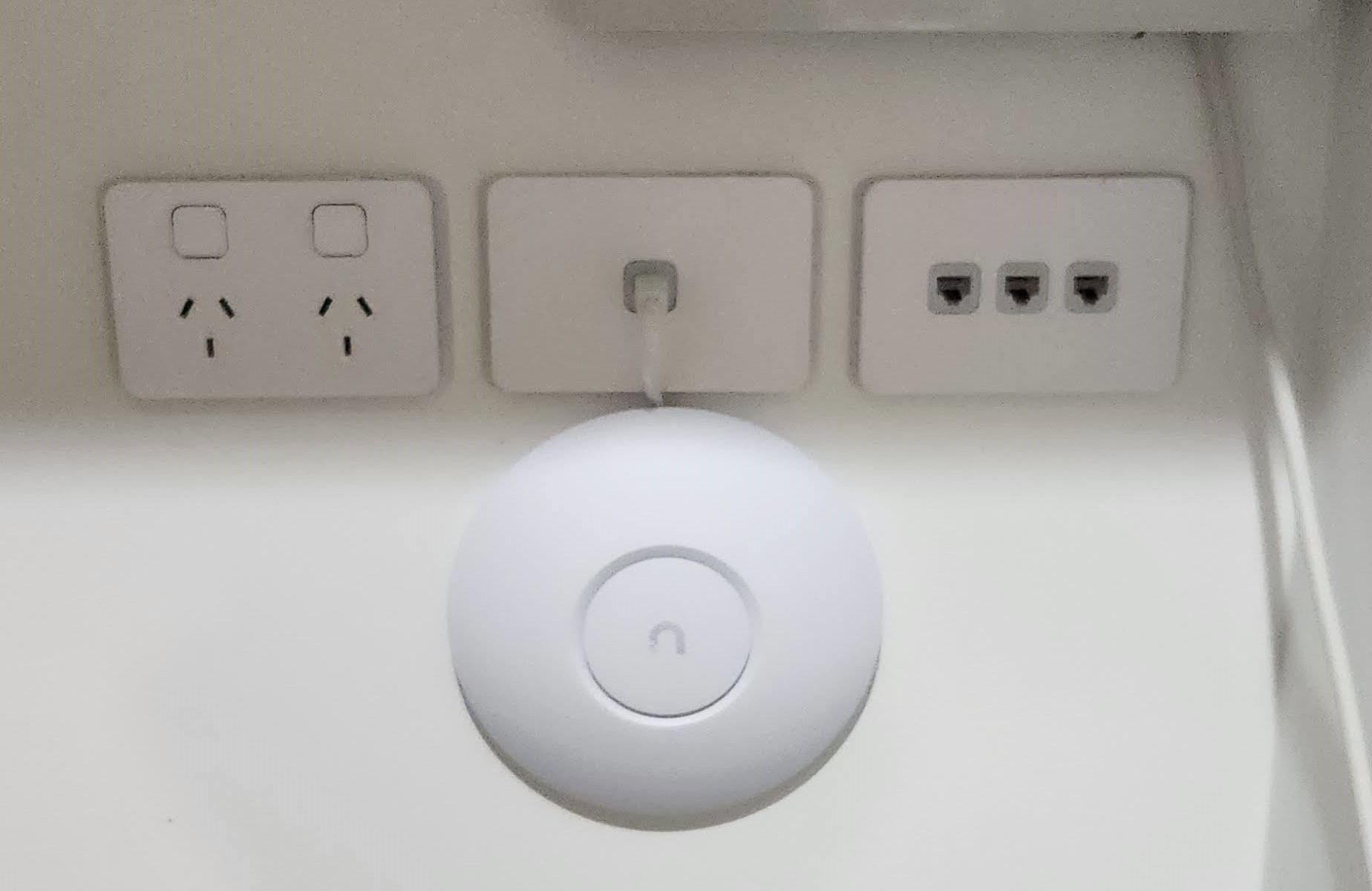
The Best Way To Extend Your WiFi: WiFi Access Points
In the realm of networking, a WiFi access point (AP) is a pivotal hardware device that bridges wireless devices to a wired network, using radio frequencies to establish connectivity. This device is essential in creating a wireless local area network (WLAN) or connecting to an existing wired network, such as Ethernet. The AP serves as the central transmitter and receiver of wireless radio signals.
Main Functions of a WiFi Access Point:
-Connectivity: It allows WiFi devices to join a wired network, enabling devices to access the internet or other network resources.
-Coverage: APs can extend the wireless coverage of a network, ensuring that connectivity reaches all corners of a space, eliminating dead spots.
-Capacity: They support multiple wireless connections simultaneously, making efficient use of the wired network connection.
Advantages of Using WiFi Access Points:
-Scalability: Easily add more APs to handle an increasing number of wireless devices without degrading performance.
-Flexibility: Accommodate a variety of devices and usage scenarios, from small home networks to large enterprise environments.
-Management: Centralized management of network settings and policies, especially when deploying multiple APs.
WiFi access points are integral to modern networking, offering a seamless and efficient way to integrate wireless devices into a network. Whether for personal use or within a corporate setting, understanding the role and functionality of APs is crucial for anyone looking to establish or expand a wireless network.
The choice between a Wi-Fi extender, mesh system and WiFi Access Points depends on several factors, including the size and layout of your home, the number of devices connected to your network, and your budget. If you're experiencing dead zones in a small to medium-sized home, a Wi-Fi extender or mesh system might be a sufficient and cost-effective solution. For larger homes with many connected devices, investing in a professionally installed WiFi Access Point System is the best solution.